You want to know more about flowering plants. They’re everywhere, right? But what makes them special? You see flowers, but do you know how they grow? They start as seeds and go through a life cycle that’s pretty amazing. Pollination is a big part of this. Without it, we wouldn’t have fruits or new plants. In this article, we’ll break down the life cycle of flowering plants. We’ll explain how seeds become flowers and how pollination and fertilization work. Let’s dive in and explore together!
Understanding Flowering Plants: A Comprehensive Guide
Flowering plants, or angiosperms, are one of the most diverse groups in the plant kingdom. They range from tiny herbs to towering trees, and they dominate many ecosystems around the world. But what exactly makes flowering plants so special?
What Are Flowering Plants?
Flowering plants are distinguished by their ability to produce “flowers,” the reproductive structures that facilitate the transfer of pollen for fertilization. These plants are crucial to many ecosystems as they provide food, oxygen, and habitat for countless organisms.
Key Characteristics of Flowering Plants
Flowering plants possess a range of characteristics that set them apart. The most notable is their production of “seeds” encased within a “fruit.” This fruit not only protects the seeds but also aids in their dispersal. In addition, flowering plants often exhibit broad leaves and complex root systems that enable them to thrive in diverse environments.
The Life Cycle of Flowering Plants
The life cycle of a flowering plant is a fascinating journey from seed to flower and back to seed again. This process involves several stages, each critical to the plant’s survival and reproduction.
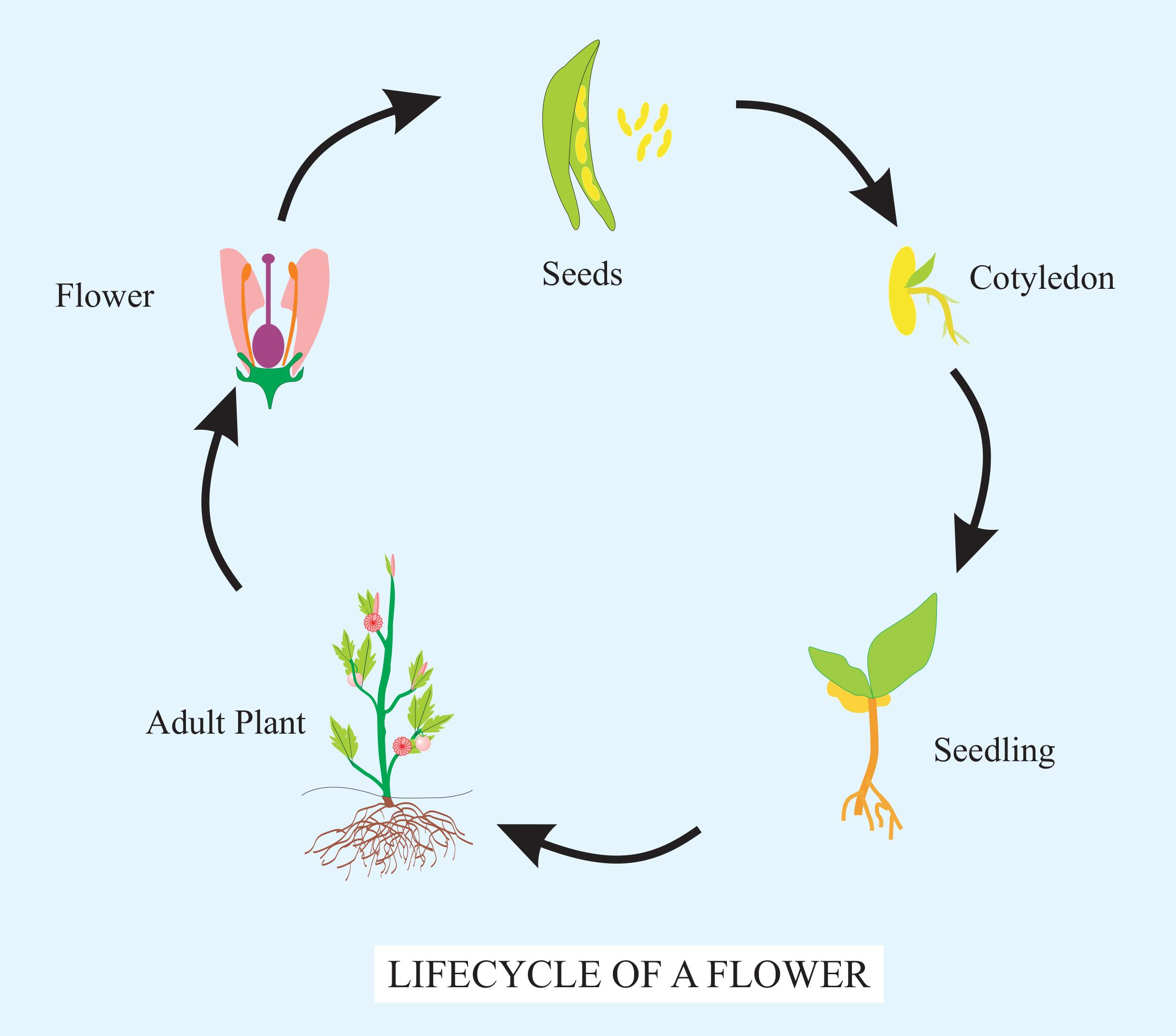
Stages of Development: From Seed to Flower
Flowering plants begin their life as a seed, which contains the embryonic plant and a food source. Under the right conditions, the seed “germinates,” sending out roots and shoots. As the plant grows, it eventually produces “flowers,” which are essential for reproduction.
The Role of Pollination
Pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred from the male part of the flower (stamen) to the female part (pistil). This can occur via wind, water, or animals, such as bees. Once pollination occurs, fertilization follows, leading to the formation of seeds within a fruit.
Structure of a Flower
A flower is more than just a pretty face; it’s a complex structure designed for reproduction.
Anatomy of a Flower
Each part of a flower has a specific role. The petals attract pollinators, while the sepals protect the developing bud. The stamens produce pollen, and the pistil is where fertilization occurs.
Function of Each Floral Organ
- Petals: Attract pollinators with their color and scent.
- Stamens: Produce pollen grains, which contain male gametes.
- Pistil: Houses the ovules, which become seeds after fertilization.
- Sepals: Protect the flower bud before it opens.
Pollination and Fertilization in Flowering Plants
Types of Pollinators
Different flowers are adapted to attract specific pollinators, whether they be insects like bees and butterflies, birds such as hummingbirds, or even the wind.
Environmental Factors
Temperature, humidity, and the presence of pollinators all impact the success of pollination and fertilization. Without proper pollination, many plants would fail to produce seeds and reproduce.

Adaptations of Flowering Plants
Flowering plants have evolved various adaptations to survive and reproduce in their environments.
Adaptations for Pollination
Brightly colored petals, enticing scents, and nectar rewards are all strategies to attract pollinators. Some plants have evolved specific structures to accommodate certain pollinators, ensuring that their pollen is effectively transferred.
Climate and Environmental Adaptations
In different climates, flowering plants may develop thicker leaves, deeper roots, or special mechanisms to conserve water. These adaptations enable them to survive in challenging environments like deserts or tropical rainforests.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-901482062-6470b1099c6a47a881f9a22d7bca0d0a.jpg)
Flowering Plants in Human Life
Flowering plants play a significant role in human culture and economy.
Economic Importance
Flowering plants are vital in agriculture, providing fruits, vegetables, and grains that are staple foods worldwide. They are also important in horticulture, where they are cultivated for ornamental purposes.
Medicinal Uses
Many flowering plants are sources of essential medicines. For example, the willow tree (a flowering plant) led to the development of aspirin, a widely used pain reliever.
Conservation and Threats to Flowering Plants
Despite their importance, many flowering plants face threats from human activities.
Impact of Habitat Loss
Deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture can lead to habitat loss, putting many flowering plant species at risk. This loss of habitat not only affects the plants themselves but also the animals and insects that depend on them.
Conservation Efforts
To protect flowering plants, conservationists work to preserve their natural habitats, create seed banks, and restore ecosystems where these plants can thrive.
Flowering plants are essential to life on Earth. They not only beautify our world but also sustain it by providing food, oxygen, and habitats. As you explore the fascinating world of flowering plants, remember their significance in ecosystems and human life. If you’re curious to learn more or have questions, feel free to leave a comment or explore other articles on our site.
Conclusion:
Flowering plants are vital to our world. They feed us, beautify our surroundings, and support countless species. Understanding their life cycle and the role of pollination helps us appreciate their importance. If you found this article helpful, leave a comment, share it, or check out more content on our website. Keep learning and exploring!
What are flowering plants?
Flowering plants, also known as angiosperms, are plants that produce flowers as their reproductive structures. These plants are characterized by their ability to develop seeds enclosed within a fruit. They represent the largest group of plants on Earth, encompassing a vast diversity of species from tiny wildflowers to majestic trees. Flowering plants play a critical role in ecosystems by providing food and habitat for various organisms and contributing to the oxygen-carbon dioxide balance of our atmosphere.
How do flowering plants reproduce?
Flowering plants reproduce through a process that involves several key stages: pollination, fertilization, and seed dispersal. Pollination occurs when pollen from the male part of a flower (stamen) is transferred to the female part (pistil). This can be achieved through various agents, including insects, wind, or water. Once pollination is successful, fertilization takes place, leading to the development of seeds within the flower’s ovary. These seeds are then dispersed by various methods, such as wind, animals, or water, to grow into new plants.
What types of flowering plants are there?
Flowering plants are categorized into two main groups: monocots and dicots. Monocots, such as grasses and lilies, are characterized by having one seed leaf (cotyledon) and parallel-veined leaves. Dicots, including roses and sunflowers, have two seed leaves and typically feature net-veined leaves. Within these categories, flowering plants further diversify into numerous species, each adapted to different environments and ecological niches.
Why are flowering plants important?
Flowering plants are crucial for several reasons. Ecologically, they provide essential resources for other organisms, including nectar for pollinators and food for herbivores. Economically, they contribute to industries such as agriculture and horticulture by supplying fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. Environmentally, they help in stabilizing soils, preventing erosion, and improving air quality through their photosynthetic processes. Their aesthetic value also enhances human well-being and enriches landscapes.
How can I care for flowering plants?
Caring for flowering plants involves understanding their specific needs, which can vary widely among species. Generally, ensure they receive adequate light, appropriate watering, and well-drained soil. Regular fertilization supports healthy growth and blooming. Additionally, pruning dead or diseased parts of the plant can promote better air circulation and prevent pest infestations. Tailoring care routines to the individual requirements of each plant species will help maintain their health and vitality.







